Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 49 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2023-10-20 Origin: Site
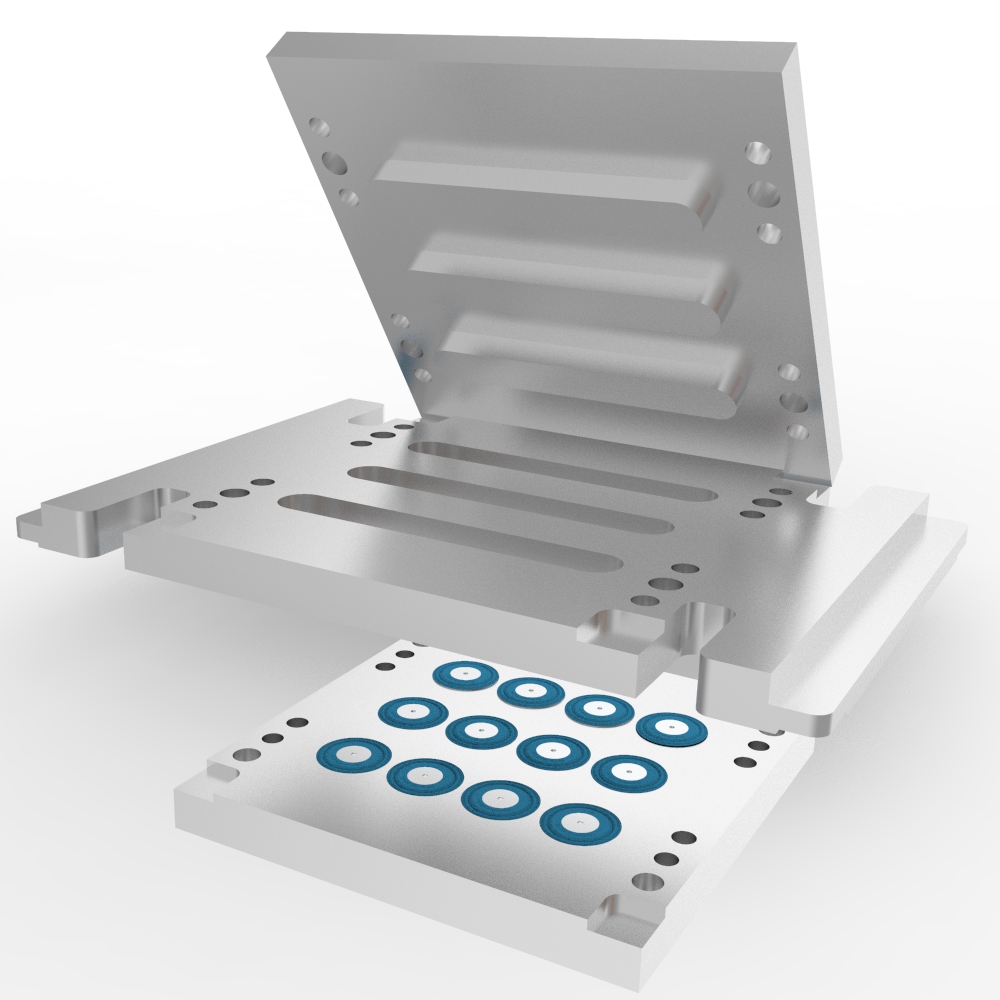
What is Transfer Molding?
Transfer molding is a manufacturing process that combine the features of both injection molding and compression molding. It involves the use of a pre-measured amount of raw material. It is heated and loaded into a chamber known as the pot situated at the top of the mold. The material contained in the pot, which is typically a heated reservoir, is used for a single cycle and can be polymer into a preheated mold through a channel referred to as a sprue. The mold remains in a closed position until the material contained within has fully cured.
How Does Transfer Molding Work?
● A piece of uncured rubber is placed into a portion of the mold.
● The mold is closed up and under hydraulic pressure, the rubber is forced through a small hole into the cavity. The mold is held closed while the rubber cures.
● The plunger is raised up and the transfer pad material is removed.
● Mold is opened and the part can be removed.
Transfer molding is a process that combines compression and transfer of the polymer charge. It involves transferring a pre-weighed polymer charge to a mold cavity feed, but it is not directly injected into the mold cavity. Instead, it is introduced into the mold cavity under the pressure of a plunger. The molded part is then ejected using an ejector pin after the resin has had time to cure. Normal post-processing requirements include trimming off the sprue and gate.
Transfer Molding VS. Compression Molding & LSR Injection Molding
Transfer Molding VS. Compression Molding
Mold Rate
The taw material used in compression molding doesn't have to be completely liquid it can be semi-solid. The semi-solid raw material can be injected or otherwise forced into the mold cavity by the plunger. This makes transfer molding faster than many other molding processes, particular those that only support liquefied material.
Dimensional Tolerance
Transfer molding allows for higher tolerance, this is due to the fact that transfer molding uses more pressure than compression molding. Both types of molding processes involve the use of pressurized raw material. With compression molding, through, the raw material is pressurized as it's injected into the mold cavity. Transfer molding, through, applies more pressure to the raw material, thereby allowing for higher dimensional tolerance.
Efficiency
Transfer mold with high efficiency and is suitable for thicker and larger parts and the cycle time is shorter than compression mold.
Costs
Transfer mold is more expensive than compression mold, as transfer mold adds needle valves cost.
Maintenance
Transfer mold is difficult to clean and maintain compared to compression mold.
Transfer Molding VS. LSR Injection Molding
Transfer molding (along with compression molding) is commonly used of different type of silicone called high consistency rubber (HCR). HCR's higher viscosity makes that particular silicone unsuitable for injection molding. Like injection molding, transfer molding pushes material into a mold through a sprue, and using a plunger rather than a screw injrctor.
1. Transfer Molding Has High Cavity Count.
Transfer molding typically has dozens of cavities, while LSR injection molding has only few cavities.
2. Transfer Molding Has Fewer Restrictions on Raw Material.
The transfer molding can produce rubber and silicone productions, while the LSR injection molding can only produce silicone productions.
3. Transfer Molding Has Lower Molding Cost.
LSR injection molding has more complex structure than transfer molding, so the molding cost is much higher than transfer molding.
Transfer Molding's Advantages
1. Allows for the easy integration of inserts, such as metal components of electronic parts, into the molded products.
2. Allows for intricate designs with sharper edges, providing greater design flexibility compared to other molding methods.
3. Allows for producing parts with minimal or no burr, eliminating the need for additional deburr processes.
4. Allows for higher tolerances. Because it applies more pressure to the raw material, thereby allowing for higher dimensional tolerances.
5. Lower tooling and equipment costs, because simpler pot and plunger design.
Transfer Molding's Disadvantages
1. Material wastage, particularly during the preparation and transfer stages. This is promarily due to the use of sprue and overflow grooves, which can result in excess material that is not conductive to recycling thermosetting polymers into the process.
2. Slower production rate than LSR injection molding, due to the additional steps involved in material preparation and transfer.
3. Air trapping may develop.
4. Complex molds, tooling can become expensive.
Contact Us / Product Inquire / Liquid Injection Molding / LSR Molding / Article Inquire / FAQ / Download / Sign In / Register / Gallery / China Hot Products / Hot Products / Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding / Customized service / Request Quote / LSR Mold Design Guide / Liquid Silicone Rubber / Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding / Food Grade Liquid Silicone Rubber / Medical Grade Liquid Silicone Rubber / LSR Seal / Expo News / Industry News / Liquid Injection Molding - Better Silicone Project News / Silicone Materail Certifications / Silicone Umbrella Valves Drawing